The Enigmatic World of CGI Cats: A Comprehensive Analysis
Introduction
In the vast landscape of computer-generated imagery, few creations have charmed viewers as consistently as the digital cat. These virtual felines appear everywhere from blockbuster films to mobile apps, winning affection across age groups. This overview traces their journey from early experiments to today’s photorealistic stars, highlighting the artistry and technology that bring them to life.
The Evolution of CGI Cats
Early Beginnings
Pioneers of computer animation first tested furry characters in short demonstrations during the 1970s. Though simple by modern standards, those rudimentary models proved that convincing hair and whiskers were possible, setting the stage for later breakthroughs.
Technological Advancements
Steady improvements in rendering power, shading algorithms, and grooming tools have pushed digital cats far beyond their blocky ancestors. Modern pipelines combine high-resolution sculpting, physics-based fur simulation, and subtle muscle systems to deliver performances that rival footage of real animals.
The Impact of CGI Cats
Cultural Phenomenon
From reaction gifs to plush toys, stylized CGI cats dominate social feeds and store shelves. Their blend of independence and playfulness mirrors the traits people already love in household pets, making them instantly shareable across cultures.
Emotional Connection
Audiences readily project feelings onto expressive animated cats because the characters echo familiar feline behaviors—curious head tilts, slow blinks, and sudden bursts of energy. Carefully timed sound design and animation curves amplify this bond, turning pixels into personalities viewers care about.
Economic Impact
Popular digital cats drive ticket sales, streaming views, and licensed merchandise, supporting thousands of jobs in design, software development, and marketing. Each successful character can spawn multi-year campaigns that extend revenue long after the initial release.
The Technology Behind CGI Cats
3D Modeling
Artists start by sculpting a clean base mesh that captures feline proportions, then add layers of anatomical detail such as skin folds and paw pads. Reference photos and video of real cats guide every decision, ensuring the silhouette reads instantly as “cat” before fur is ever applied.
Texturing
Specialized shaders replicate the way light scatters within individual hairs, producing natural color shifts along each strand. Hand-painted maps control length, density, and clumping, while procedural noise breaks up uniformity for a believable, slightly messy coat.
Rigging and Animation
A flexible skeleton lets animators bend the spine into characteristic stretches and pounces. Control rigs for ears, whiskers, and tail communicate mood with minimal keyframes, and motion-capture data from trained animals can be retargeted to add organic nuance.
Rendering
Final frames are calculated in powerful render farms that simulate millions of hair-to-hair interactions, subsurface scattering on skin, and micro-shadows at the base of each follicle. Optimized sampling strategies keep render times manageable without sacrificing softness and depth.
Case Studies: Notable CGI Cats
Puss in Boots
This swashbuckling orange tabler, first introduced in a fairy-tale spin-off, showcases confident swagger through exaggerated posing and secondary motion on his cape and plume. His success underlined how a supporting character can headline a franchise when animation and voice work align.
Whiskers
A side character in a metropolitan pet comedy, Whiskers wins laughs with deadpan stares and perfectly timed ear twitches. Subtle rig controls let the animators shift him from aloof to alarmed in a single frame, proving that small physical jokes can steal entire sequences.
Conclusion
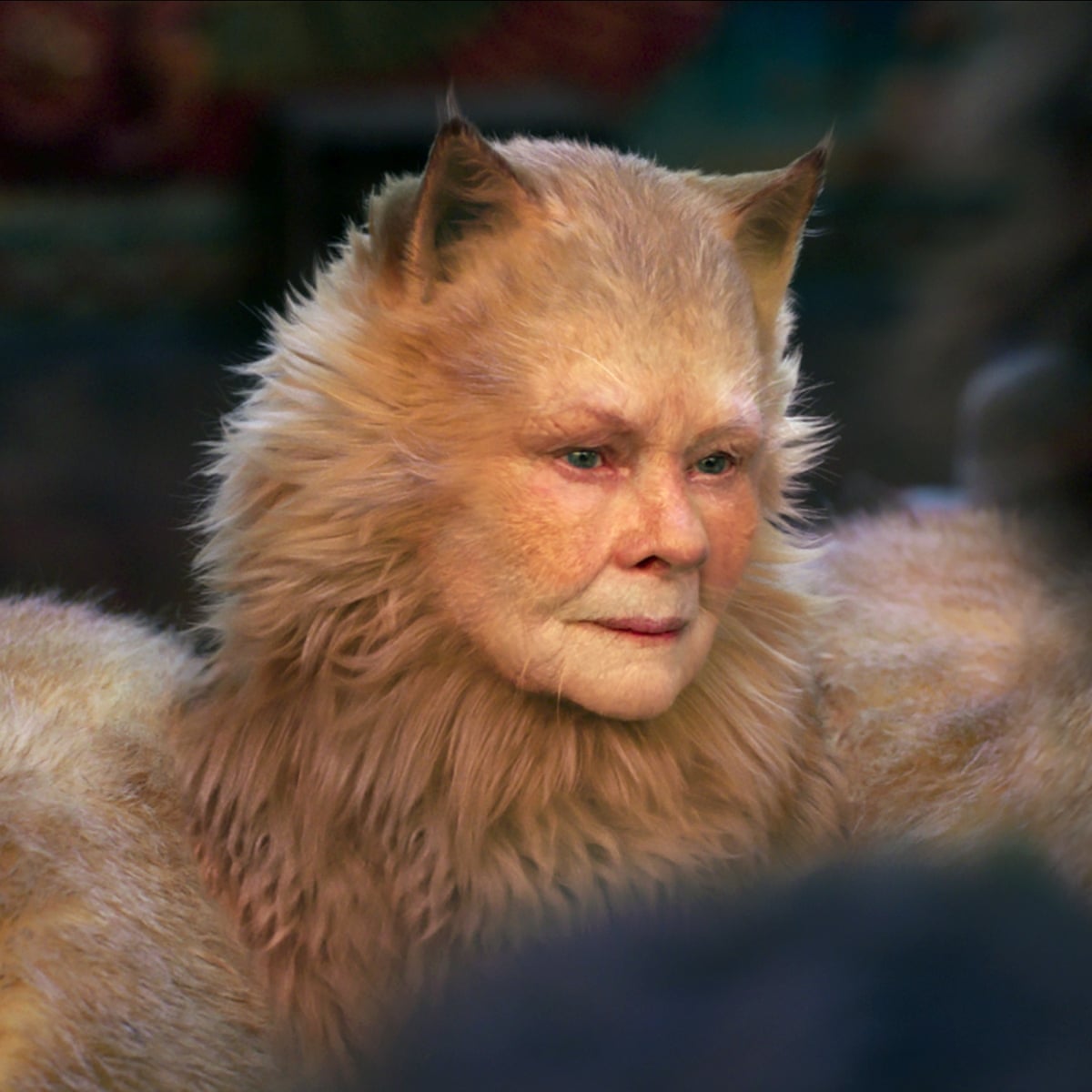

From experimental wireframes to scene-stealing stars, CGI cats have carved out a lasting niche in entertainment. Their continued popularity rests on a mix of technical craft and universal affection for feline quirks. As tools grow faster and more intuitive, audiences can expect even richer performances from these digital companions.
Recommendations and Future Research
To keep pushing realism and appeal, studios and researchers are encouraged to explore the following directions:
1. Advanced Grooming Systems: Develop hair shaders that respond dynamically to wind, moisture, and contact, reducing the need for shot-specific fixes.
2. AI-Assisted Motion: Use machine-learning models trained on extensive feline video reference to propose baseline locomotion and facial micro-expressions.
3. Emotional Fidelity: Study subtle ear and tail cues alongside eye dilation patterns to build libraries that help animators hit precise emotional beats faster.

Pursuing these goals will ensure that the next generation of CGI cats remains as captivating—and as comforting—as the ones audiences already adore.

